Scientists and engineers at UNSW Sydney, who previously developed a method for making green ammonia, have now turned to artificial intelligence and machine learning to make the process even more efficient.
Ammonia, a nitrogen-rich substance found in fertilizer, is often credited with saving much of the world from famine in the 20th century. But its benefit to humankind has come at a cost, with one of the largest carbon footprints of all industrial processes.
[…]
But in 2021, a UNSW team discovered a way to make ammonia from air and water using renewable energy, at about the same temperature as a warm summer’s day.


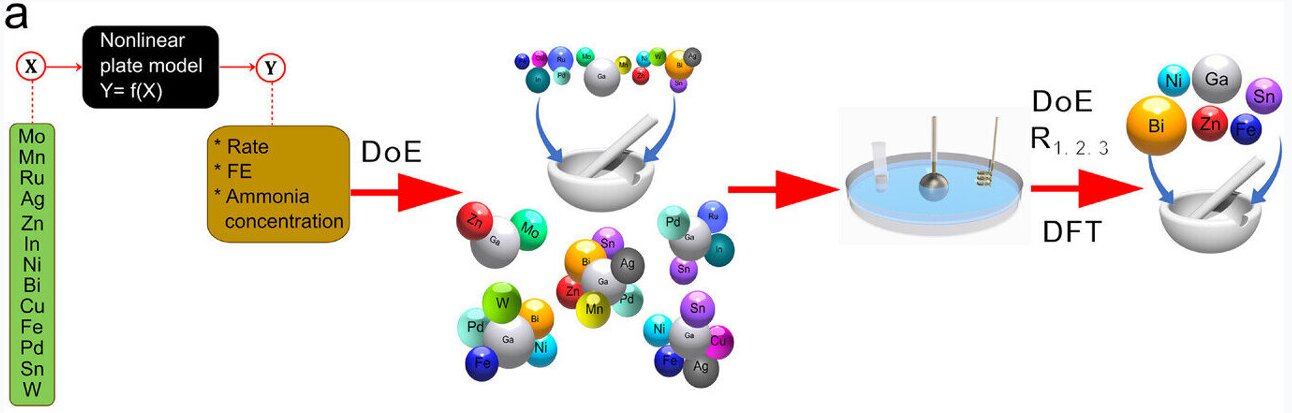
Yeah computational chemistry is such an underrated application of AI compared to all the chatbots and image generators - the fact that it narrowed down 8000 options to ONE viable catalyst is insanley efficient and probably saved years of lab work.